Matlab 官方提供了完整的单目视觉 vSLAM 的 pipeline,https://www.mathworks.com/help/vision/ug/monocular-visual-simultaneous-localization-and-mapping.html。这里对 Matlab 的这边文章的关键点做一个笔记和讨论,具体的实现可以参考原文文档。
初始化数据集
Matlab 提供了imageDatastore类用于初始化图像存储集合,其接受一个图像的文件夹路径的参数。
imageFolder = [dataFolder,'rgbd_dataset_freiburg3_long_office_household/rgb/'];
imds = imageDatastore(imageFolder);
初始化地图
在 SLAM 管线中,首先我们应该对相机进行标定,相机标定可以用Computer Vision 工具箱中的相机标定工具。如果预先知道了相机的内参,可以通过cameraIntrinsics类直接进行初始化。
% Create a cameraIntrinsics object to store the camera intrinsic parameters.
% The intrinsics for the dataset can be found at the following page:
% https://vision.in.tum.de/data/datasets/rgbd-dataset/file_formats
% Note that the images in the dataset are already undistorted, hence there
% is no need to specify the distortion coefficients.
focalLength = [535.4, 539.2]; % in units of pixels
principalPoint = [320.1, 247.6]; % in units of pixels
imageSize = size(currI,[1 2]); % in units of pixels
intrinsics = cameraIntrinsics(focalLength, principalPoint, imageSize);
在例子中使用的数据集已经提供了相机的标定参数,我们可以直接使用。注意,对于一般相机获取到的照片来说,我们应该进行照片的去畸变,Matlab 提供了去畸变函数undistortImage,具体用法如下
% Get intrinsic parameters of the camera
intrinsics = cameraParams.Intrinsics;
I = undistortImage(I, intrinsics);
识别并抓取图片特征
在该例子中,我们使用 ORB 特征,ORB 特征是一种广泛使用的特征,并且能够快速识别,更好的用于实时 SLAM 环境。借助helperDetectAndExtractFeatures函数,我们可以识别出图片中的特征和其对应的位置。
% Detect and extract ORB features
scaleFactor = 1.2;
numLevels = 8;
numPoints = 1000;
[preFeatures, prePoints] = helperDetectAndExtractFeatures(currI, scaleFactor, numLevels, numPoints);
进一步的,我们可以可视化图片的特征
I = readimage(imds, 1);
imshow(I);
hold on;
plot(selectStrongest(prePoints, 100));
抓取特征以后,下一步进行特征匹配,由于我们的图片是从视频流中获得的有序图片,我们保留第一张图片,并且从第二张图片开始,与第一张图片做特征匹配。当特征少于 100 个时,我们选择下一张图片与第一张图片匹配,直到找到对应的匹配图片为止。
firstI = currI; % Preserve the first frame
currFrameIdx = currFrameIdx + 1; % set current to 2
while ~isMapInitialized && currFrameIdx < numel(imds.Files)
currI = readimage(imds, currFrameIdx);
currFrameIdx = currFrameIdx + 1;
[currFeatures, currPoints] = helperDetectAndExtractFeatures(currI, ...
scaleFactor, numLevels, numPoints);
indexPairs = matchFeatures(preFeatures, currFeatures, Unique=true, ...
MaxRatio=0.9, MatchThreshold=40);
minMatches = 100;
if size(indexPairs, 1) < minMatches; continue; end
% ...
找到对应的图片以后,我们利用对极约束求解Homography和基础矩阵Fundamental matrix。当场景为平面时,Homography比基础矩阵更容易匹配。
% Select the model based on a heuristic
ratio = scoreH/(scoreH + scoreF);
ratioThreshold = 0.45;
if ratio > ratioThreshold
inlierTformIdx = inliersIdxH;
tform = tformH;
else
inlierTformIdx = inliersIdxF;
tform = tformF;
end
我们根据匹配的结果选择对应的Homography或者Fundamental matrix。这里inlierTformIdx表示用于求解的特征点的下标,tfrom则是对应的变换矩阵。
相对位姿估计
在得到对应的变换矩阵的求解点(inlier)以后,我们可以进行相对位姿估计。我们用一半的特征点进行估计,用来减少估计的成本。
% Computes the camera location up to scale. Use half of the
% points to reduce computation
inlierPrePoints = preMatchedPoints(inlierTformIdx);
inlierCurrPoints = currMatchedPoints(inlierTformIdx);
[relPose, validFraction] = estrelpose(tform, intrinsics, ...
inlierPrePoints(1:2:end), inlierCurrPoints(1:2:end));
% If not enough inliers are found, move to the next frame
if validFraction < 0.9 || numel(relPose)==3
continue
end
如果validFraction太小,一般来说小于 0.9,那就意味着基础矩阵是不正确的。或者如果我们的相对位姿计算不正确,那我们就应该跳过该图片,利用下一张图片求解。
三角化和稀疏点云估计
当我们获得了相对位姿以后,我们可以利用三角化求解稀疏点云。当我们的两张图片过于靠近时,可能会出现退化问题,于是我们将退化的位姿过滤。
% Triangulate two views to obtain 3-D map points
minParallax = 1; % In degrees
[isValid, xyzWorldPoints, inlierTriangulationIdx] = helperTriangulateTwoFrames(...
rigidtform3d, relPose, inlierPrePoints, inlierCurrPoints, intrinsics, minParallax);
if ~isValid
continue
end
初始化结果
至此,我们完成了整个的地图的初始化工作,我们可以查看对应的图片和初始化效果。根据运行的结果,我们可以看到最后使用了第 1 张和第 29 张图片完成了地图的初始化工作。初始化的特征匹配结果如下
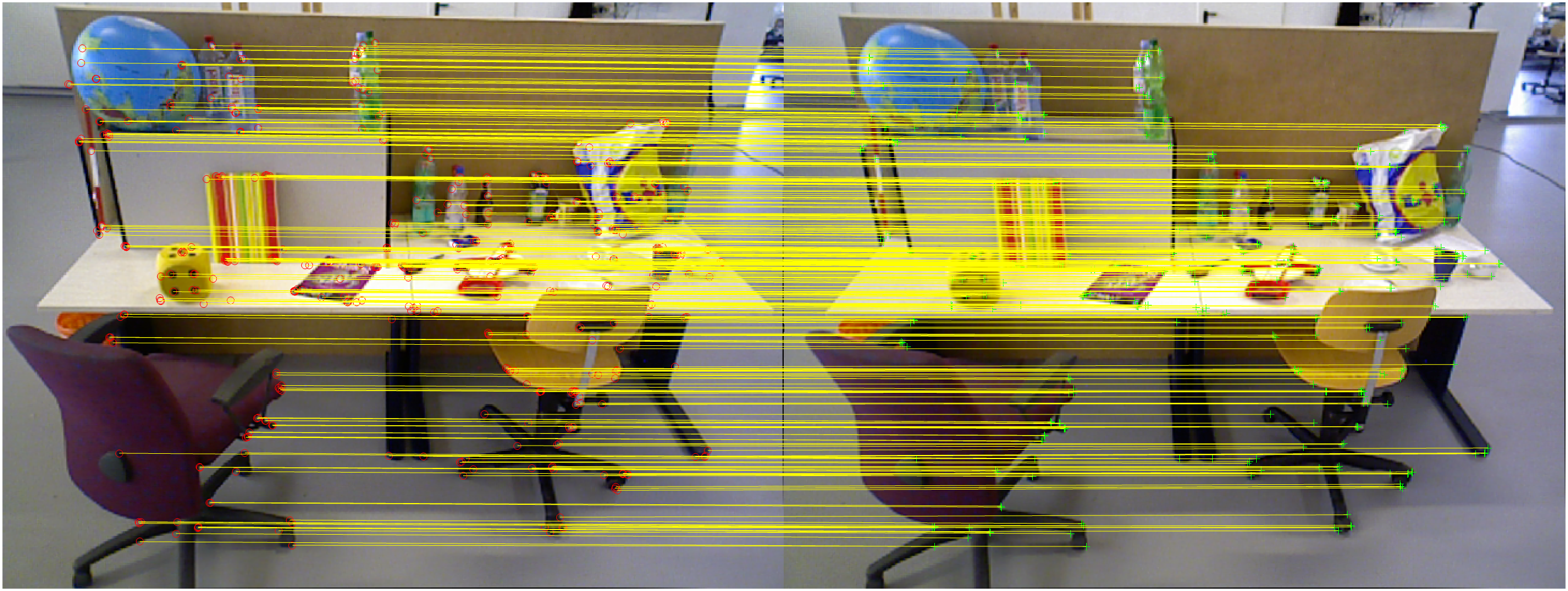

建立关键帧和地图空间点存储集合
Matlab 提供了两个类来存储关键帧和地图空间点,分别是imageviewset和worldpointset。我们创建关键帧viewset以后,将用于地图初始化的两张图片作为初始的俩个关键帧存入,同时我们加入关键帧相关性链接。相关性指的是俩个关键帧之间的相对位姿,以及相关的匹配点。最后我们将三角化后的世界坐标加入到地图的世界点集合中。
vSetKeyFrames = imageviewset;
mapPointSet = worldpointset;
preViewId = 1;
vSetKeyFrames = addView(vSetKeyFrames, preViewId, rigidtform3d, Points=prePoints,...
Features=preFeatures.Features);
currViewId = 2;
vSetKeyFrames = addView(vSetKeyFrames, currViewId, relPose, Points=currPoints,...
Features=currFeatures.Features);
vSetKeyFrames = addConnection(vSetKeyFrames, preViewId, currViewId, relPose, Matches=indexPairs);
[mapPointSet, newPointIdx] = addWorldPoints(mapPointSet, xyzWorldPoints);
这里newPointIdx是添加的世界点的下标集合。每一个世界点都是有两帧关键帧的匹配点通过对极几何约束和三角化处理得到,因此在indexPairs中的第一组点对应的第一关键帧中的点序列,第二组点对应的是第二个关键帧中的点序列。在mapPointSet中,我们需要将这一组对应关系添加进去,之后的后端优化中,我们将使用到世界点和像点的对应关系。
mapPointSet = addCorrespondences(mapPointSet, preViewId, newPointIdx, indexPairs(:,1));
mapPointSet = addCorrespondences(mapPointSet, currViewId, newPointIdx, indexPairs(:,2));
回环检测和初始化地标识别数据库
我们初始化地标识别数据库用于回环检测算法。地标识别使用的是词袋模型。我们可以从一个大数据采集的图像集合中生成字典,生成的方法为
bofData = bagOfFeatures(imds, ...
CustomExtractor=@helperORBFeatureExtractorFunction, ...
TreeProperties=[3, 10], StrongestFeatures=1);
在这里我们使用一个预生成的字典文件,并且生成回环检测数据库
bofData = load("bagOfFeaturesDataSLAM.mat");
loopDatabase = invertedImageIndex(bofData.bof,SaveFeatureLocations=false);
接下来,我们将第一帧和第二帧的特征数据以及viewId添加到数据库。
addImageFeatures(loopDatabase, preFeatures, preViewId);
addImageFeatures(loopDatabase, currFeatures, currViewId);
第一次后端优化和重建可视化
当我们有了世界点的坐标,位姿以及成像坐标以后,我们可以使用bundleAdjustment对数据进行优化,寻找最佳的位姿以达到最少的重投影误差。Matlab 内建了bundleAdjustment函数,我们需要输入世界点的坐标,视图中相关联的对应点tracks,相机位姿信息,相机内参。同时,我们可以指定哪些关键帧的位姿是不需要调整的,在这里我们第一帧的位置将会被固定。我们第一次后端优化仅仅使用了俩个关键帧,在双视图几何中,俩个相对应的像点,形成一个世界空间的三位点,因此xyzWorldPoints的大小应该和tracks的大小一致,并且每个tracks中的点对,成像一个xyzWorldPoints中的点。
tracks = findTracks(vSetKeyFrames);
cameraPoses = poses(vSetKeyFrames);
[refinedPoints, refinedAbsPoses] = bundleAdjustment(xyzWorldPoints, tracks, ...
cameraPoses, intrinsics, FixedViewIDs=1, ...
PointsUndistorted=true, AbsoluteTolerance=1e-7,...
RelativeTolerance=1e-15, MaxIteration=20, ...
Solver="preconditioned-conjugate-gradient");
在bundleAdjustment之后,我们得到了调整后的点以及调整后的相机位姿态。我们应该将调整后的点重新应用到我们的关键帧中。为了可视化方便,我们将坐标点和位姿的都按统一尺度进行缩放
% Scale the map and the camera pose using the median depth of map points
medianDepth = median(vecnorm(refinedPoints.'));
refinedPoints = refinedPoints / medianDepth;
refinedAbsPoses.AbsolutePose(currViewId).Translation = ...
refinedAbsPoses.AbsolutePose(currViewId).Translation / medianDepth;
relPose.Translation = relPose.Translation/medianDepth;
% Update key frames with the refined poses
vSetKeyFrames = updateView(vSetKeyFrames, refinedAbsPoses);
vSetKeyFrames = updateConnection(vSetKeyFrames, preViewId, currViewId, relPose);
% Update map points with the refined positions
mapPointSet = updateWorldPoints(mapPointSet, newPointIdx, refinedPoints);
% Update view direction and depth
mapPointSet = updateLimitsAndDirection(mapPointSet, newPointIdx, vSetKeyFrames.Views);
% Update representative view
mapPointSet = updateRepresentativeView(mapPointSet, newPointIdx, vSetKeyFrames.Views);
mapPlot = helperVisualizeMotionAndStructure(vSetKeyFrames, mapPointSet);
最后我们将位姿和世界点绘图得到
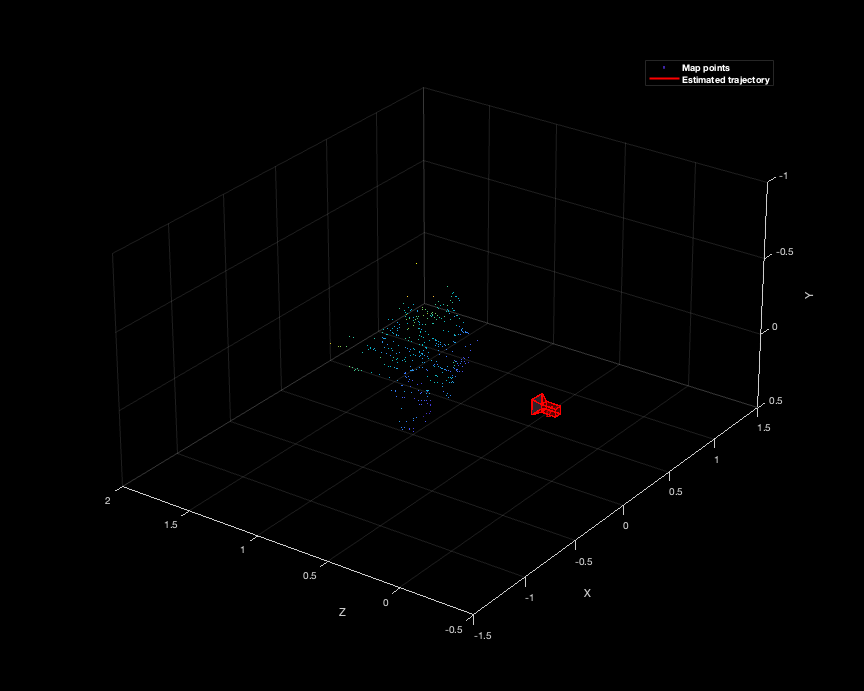
SLAM 位姿跟踪
现在我们开始实现 SLAM 的位姿跟踪。每当我们发现了一个新的关键帧,我们就将其加入到我们的数据集中,并计算和调整我们的位姿态,为了简化我们的跟踪问题,当我们检测到回环的时候,我们停止跟踪。
currKeyFrameId = currViewId;
lastKeyFrameId = currViewId;
lastKeyFrameIdx = currFrameIdx - 1;
addedFramesIdx = [1; lastKeyFrameIdx];
isLoopClosed = false;
在这里currKeyFrameId和lastKeyFrameId追踪的是关键帧的 Id,而lastKeyFrameIdx是关键帧所对应照片的 Index,我们刚刚处理了第一帧和第二帧用于地图的初始化,因此,在这里lastKeyFrameId为 2,而lastKeyFrameIdx为 29(因为第二帧关键帧来自于第 29 张照片,减 1 是因为我们在while中多加了一次)。addedFramesIdx则继续追踪被加入的照片的 Index。
现在我们开始进入追踪循环,对于每一帧来说我们进行:
- 特征匹配,我们将新的一帧和最后一帧进行匹配。
- 使用 Perspective-n-Point 算法估计新的一帧的相机位姿
- 将最后一帧的世界点重投影到新的一帧,并且寻找相匹配的点
- 执行一次
bundleAdjustment,但这一次我们只关心新的一帧的相机位姿,因此调用bundleAdjustmentMotion - 将更多的世界点重投影到新的一帧,并继续调用
bundleAdjustmentMotion - 最后,我们尝试检测新的一帧是否为关键帧,如果是则加入关键帧序列,否则继续处理下一帧数据。
很显然,当新的一帧数据的特征点不够多的时候,我们会出现追踪丢失问题,我们可以不断加入新的帧来寻找匹配的特征点(具体来说,类似我们走到了一个四面都是白墙的迷宫,我们迷路了,我们可以试探性的往某个方向,直到得到路标,然后继续追踪)。
代码表述如下
% Main loop
isLastFrameKeyFrame = true;
while ~isLoopClosed && currFrameIdx < numel(imds.Files)
currI = readimage(imds, currFrameIdx);
[currFeatures, currPoints] = helperDetectAndExtractFeatures(currI, scaleFactor, numLevels, numPoints);
% Track the last key frame
% mapPointsIdx: Indices of the map points observed in the current frame
% featureIdx: Indices of the corresponding feature points in the
% current frame
[currPose, mapPointsIdx, featureIdx] = helperTrackLastKeyFrame(mapPointSet, ...
vSetKeyFrames.Views, currFeatures, currPoints, lastKeyFrameId, intrinsics, scaleFactor);
% Track the local map and check if the current frame is a key frame.
% A frame is a key frame if both of the following conditions are satisfied:
%
% 1. At least 20 frames have passed since the last key frame or the
% current frame tracks fewer than 100 map points.
% 2. The map points tracked by the current frame are fewer than 90% of
% points tracked by the reference key frame.
%
% Tracking performance is sensitive to the value of numPointsKeyFrame.
% If tracking is lost, try a larger value.
%
% localKeyFrameIds: ViewId of the connected key frames of the current frame
numSkipFrames = 20;
numPointsKeyFrame = 80;
[localKeyFrameIds, currPose, mapPointsIdx, featureIdx, isKeyFrame] = ...
helperTrackLocalMap(mapPointSet, vSetKeyFrames, mapPointsIdx, ...
featureIdx, currPose, currFeatures, currPoints, intrinsics, scaleFactor, numLevels, ...
isLastFrameKeyFrame, lastKeyFrameIdx, currFrameIdx, numSkipFrames, numPointsKeyFrame);
% Visualize matched features
updatePlot(featurePlot, currI, currPoints(featureIdx));
if ~isKeyFrame
currFrameIdx = currFrameIdx + 1;
isLastFrameKeyFrame = false;
continue
else
isLastFrameKeyFrame = true;
end
% Update current key frame ID
currKeyFrameId = currKeyFrameId + 1;
对于每个关键帧都进行本地映射。确定新的关键帧时,将其添加到关键帧集合中,并更新新关键帧观察到的地图点的属性。为了确保mapPointSet中包含尽可能少的异常值,一个有效的地图点必须在至少 3 个关键帧中被观察到。
新的地图点是通过三角化当前关键帧及其连接的关键帧中的 ORB 特征点创建的。对于当前关键帧中的每个未匹配的特征点,使用matchFeatures在连接的关键帧中搜索与其他未匹配点的匹配点。本地束调整会优化当前关键帧的位姿、连接关键帧的位姿以及这些关键帧中观察到的所有地图点。
% Add the new key frame
[mapPointSet, vSetKeyFrames] = helperAddNewKeyFrame(mapPointSet, vSetKeyFrames, ...
currPose, currFeatures, currPoints, mapPointsIdx, featureIdx, localKeyFrameIds);
% Remove outlier map points that are observed in fewer than 3 key frames
outlierIdx = setdiff(newPointIdx, mapPointsIdx);
if ~isempty(outlierIdx)
mapPointSet = removeWorldPoints(mapPointSet, outlierIdx);
end
% Create new map points by triangulation
minNumMatches = 10;
minParallax = 3;
[mapPointSet, vSetKeyFrames, newPointIdx] = helperCreateNewMapPoints(mapPointSet, vSetKeyFrames, ...
currKeyFrameId, intrinsics, scaleFactor, minNumMatches, minParallax);
% Local bundle adjustment
[refinedViews, dist] = connectedViews(vSetKeyFrames, currKeyFrameId, MaxDistance=2);
refinedKeyFrameIds = refinedViews.ViewId;
fixedViewIds = refinedKeyFrameIds(dist==2);
fixedViewIds = fixedViewIds(1:min(10, numel(fixedViewIds)));
% Refine local key frames and map points
[mapPointSet, vSetKeyFrames, mapPointIdx] = bundleAdjustment(...
mapPointSet, vSetKeyFrames, [refinedKeyFrameIds; currKeyFrameId], intrinsics, ...
FixedViewIDs=fixedViewIds, PointsUndistorted=true, AbsoluteTolerance=1e-7,...
RelativeTolerance=1e-16, Solver="preconditioned-conjugate-gradient", ...
MaxIteration=10);
% Update view direction and depth
mapPointSet = updateLimitsAndDirection(mapPointSet, mapPointIdx, vSetKeyFrames.Views);
% Update representative view
mapPointSet = updateRepresentativeView(mapPointSet, mapPointIdx, vSetKeyFrames.Views);
% Visualize 3D world points and camera trajectory
updatePlot(mapPlot, vSetKeyFrames, mapPointSet);
循环闭合检测步骤采用本地映射过程处理的当前关键帧,并尝试检测和闭合循环。通过使用evaluateImageRetrieval查询与当前关键帧在视觉上相似的数据库图像来识别循环候选帧。如果候选关键帧与最后一个关键帧不相连且其三个相邻关键帧是循环候选帧,则该候选关键帧是有效的。
当找到一个有效的循环候选帧时,使用estgeotform3d计算循环候选帧与当前关键帧之间的相对位姿。相对位姿表示存储在affinetform3d对象中的三维相似变换。然后添加具有相对位姿的循环连接,并更新mapPointSet和vSetKeyFrames。
% Check loop closure after some key frames have been created
if currKeyFrameId > 20
% Minimum number of feature matches of loop edges
loopEdgeNumMatches = 50;
% Detect possible loop closure key frame candidates
[isDetected, validLoopCandidates] = helperCheckLoopClosure(vSetKeyFrames, currKeyFrameId, ...
loopDatabase, currI, loopEdgeNumMatches);
if isDetected
% Add loop closure connections
[isLoopClosed, mapPointSet, vSetKeyFrames] = helperAddLoopConnections(...
mapPointSet, vSetKeyFrames, validLoopCandidates, currKeyFrameId, ...
currFeatures, loopEdgeNumMatches);
end
end
% If no loop closure is detected, add current features into the database
if ~isLoopClosed
addImageFeatures(loopDatabase, currFeatures, currKeyFrameId);
end
% Update IDs and indices
lastKeyFrameId = currKeyFrameId;
lastKeyFrameIdx = currFrameIdx;
addedFramesIdx = [addedFramesIdx; currFrameIdx]; %#ok<AGROW>
currFrameIdx = currFrameIdx + 1;
end % End of main loop
回环检测和优化
在最后,当我们检测到回环以后,我们应该进行回环优化,将我们的位姿信息进一步的调整。
if isLoopClosed
% Optimize the poses
minNumMatches = 20;
vSetKeyFramesOptim = optimizePoses(vSetKeyFrames, minNumMatches, Tolerance=1e-16);
% Update map points after optimizing the poses
mapPointSet = helperUpdateGlobalMap(mapPointSet, vSetKeyFrames, vSetKeyFramesOptim);
updatePlot(mapPlot, vSetKeyFrames, mapPointSet);
% Plot the optimized camera trajectory
optimizedPoses = poses(vSetKeyFramesOptim);
plotOptimizedTrajectory(mapPlot, optimizedPoses)
% Update legend
showLegend(mapPlot);
end